Water is one of the most vital components used in all industries. It is used in a variety of industrial processes. It can be used for washing, cooling, heat exchange, condensing steam, and so on. However, industrial water is not consumed. As a result, almost all industries generate wastewater that requires immediate attention. As a result, improper wastewater discharge can pollute the local environment. Many manufacturing industries treat by-products as wastewater called “Effluent” before releasing it into the environment.
Effluent is the stream that exits a chemical reactor and is an outflow of water or gas from a natural body of water or a man-made structure. It is also known as treated or untreated waste water that flows from a treatment plant, sewage treatment plant, or industrial outlet.
So, with the help of an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP), untreated effluent is converted into Treated Effluent. This is also known as a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP). The clean water is then safely discharged into the environment.
ETP Plant – Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer in India
Industrial operations play a crucial role in the global economy, but they also generate wastewater that requires careful treatment. This is where effluent treatment plants (ETPs) come in, acting as guardians of both industrial productivity and environmental health. By effectively treating wastewater, ETP Plant ensure compliance with regulations, reduce pollution, and protect precious water resources. We offer a wide range of ETP Plants to cater to various capacities and treatment needs. Our global network of distributors, dealers, suppliers and service partners ensures we support our clients wherever they are. We’re committed to providing competitive price and flexible financing options to suit your budget.
What is Common ETP Plant (CEPT Plant)?
The process of collecting, transporting, treating, and disposing of effluents from industrial estates is known as Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP). Industrial wastewater and domestic sewage generated by industrial plants are included in the effluent. This common effluent treatment plant concept assists small and medium-sized industries in discarding/disposing of their effluents. Several business clusters in India have installed and are operating CETP Plant. They serve to reduce effluent treatment costs, increase collective treatment, and reduce land costs for small-scale business centres that cannot afford an individual treatment plant.
Types of Common Effluent Treatment Plant
The CETP Plant can be installed as a mixed effluent plant, allowing it to handle all of the various types of wastewater from the estate’s industries by utilising the various methods/steps available within the CETP. These are some examples:
- Sludge Control
- Initial Treatment
- Primary Treatment
- Following Treatment
- Treatment at the Tertiary Level
ETP Plant Process
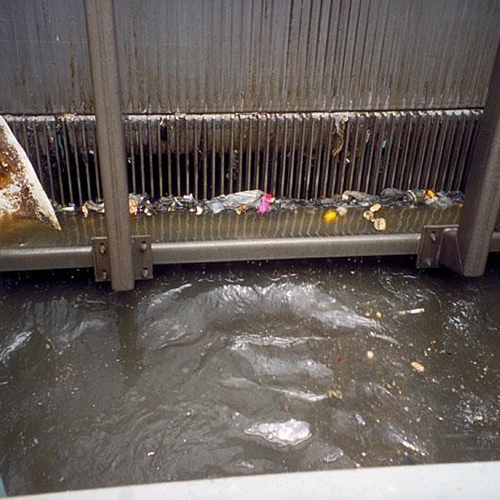
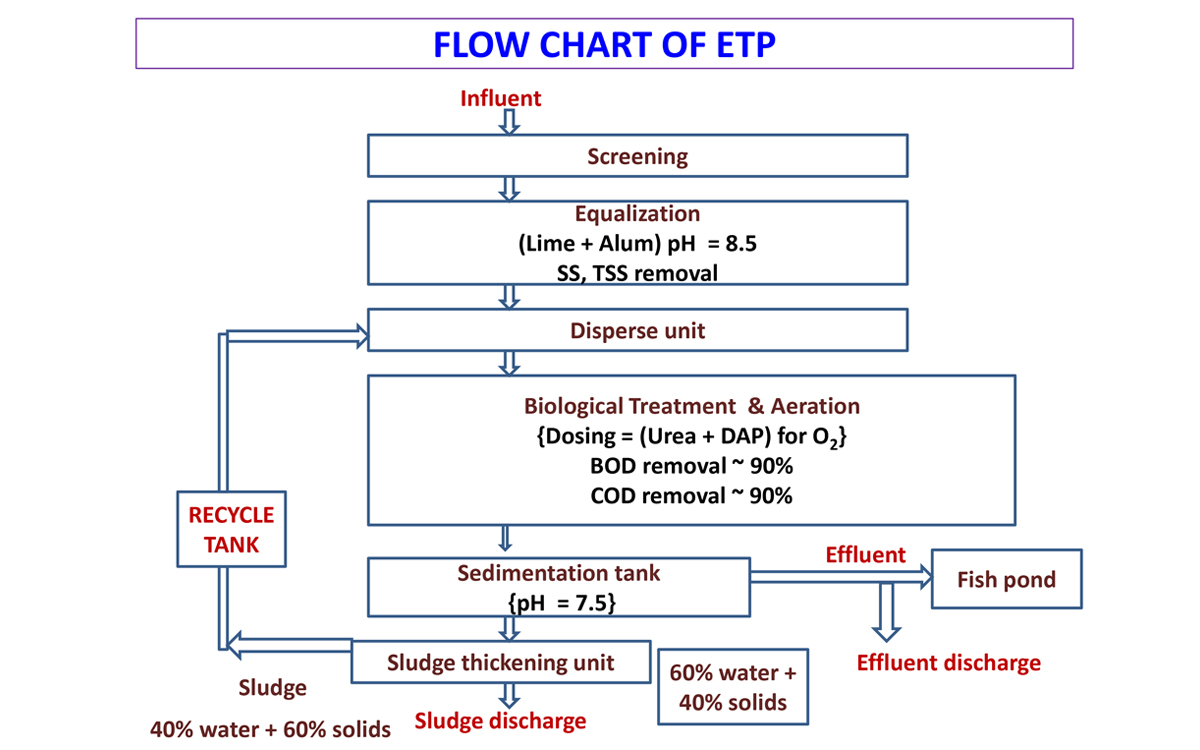
1. Screen chamber
Remove relatively large solids to avoid abrasion of mechanical equipments and clogging of hydraulic system.
2. Collection tank
The collection tank collects the effluent water from the screening chamber, stores and then pumps it to the equalization tank.
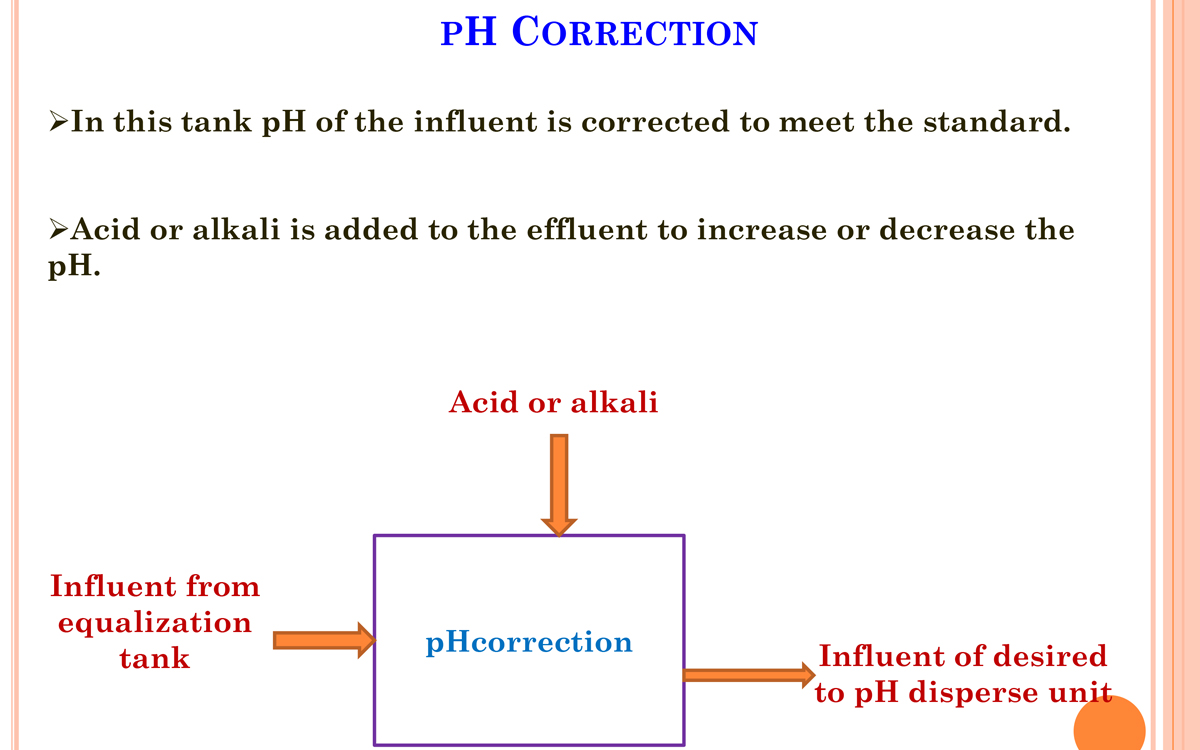
3. Equalization tank
- The effluents do not have similar concentrations at all the time; the pH will vary time to time.
- Effluents are stored from 8 to 12 hours in the equalization tank resulting in a homogenous mixing of effluents and helping in neutralization.
- It eliminates shock loading on the subsequent treatment system.
- Continuous mixing also eliminates settling of solids within the equalization tank.
- Reduces SS, TSS.


4. Flash mixer:
Coagulants were added to the effluents:
- Lime: (800-1000 ppm) To correct the pH upto 8-9
- Alum: (200-300 ppm) To remove colour
- Poly electrolyte: (0.2 ppm) To settle the suspended matters & reduce SS, TSS.
The addition of the above chemicals by efficient rapid mixing facilitates homogeneous combination of flocculates to produce microflocs.
5. Clarriflocculator:
In the clarriflocculator the water is circulated continuously by the stirrer.
- Overflowed water is taken out to the aeration tank.
- The solid particles are settled down, and collected separately and dried this reduces SS, TSS.
- Flocculation provides slow mixing that leads to the formation of macro flocs, which then settles out in the clarifier zone.
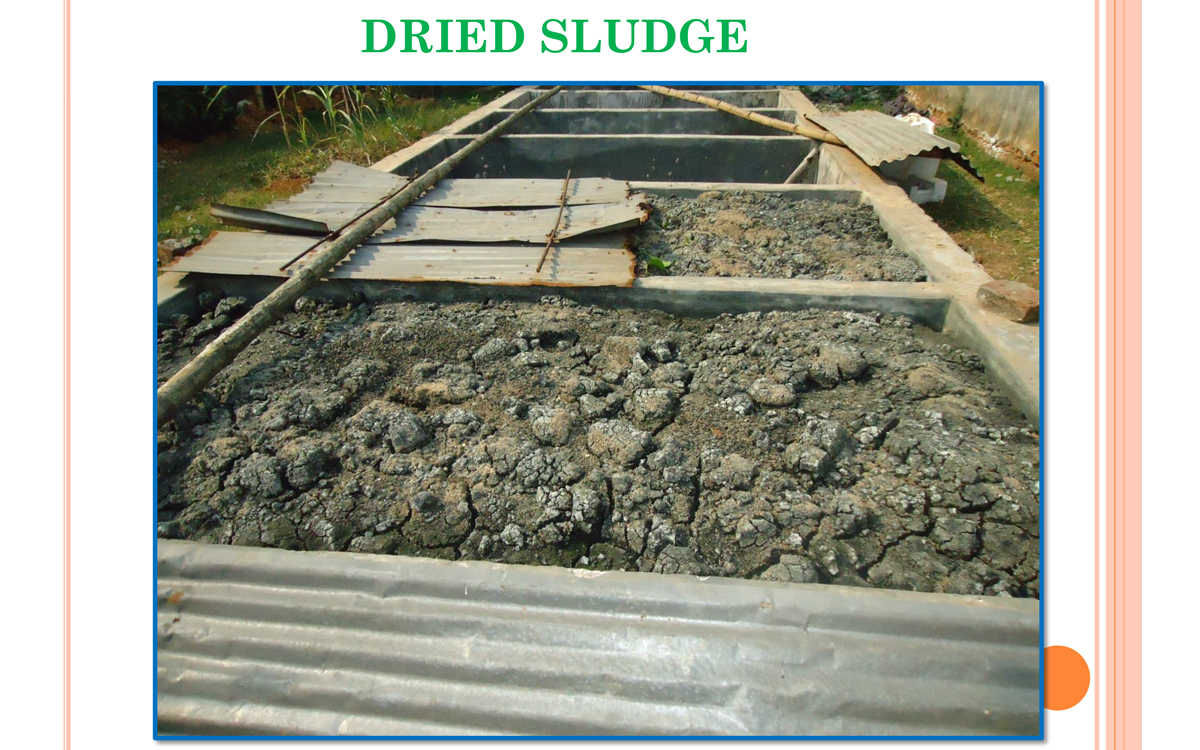
- The settled solids i.e. primary sludge are pumped into sludge drying beds.
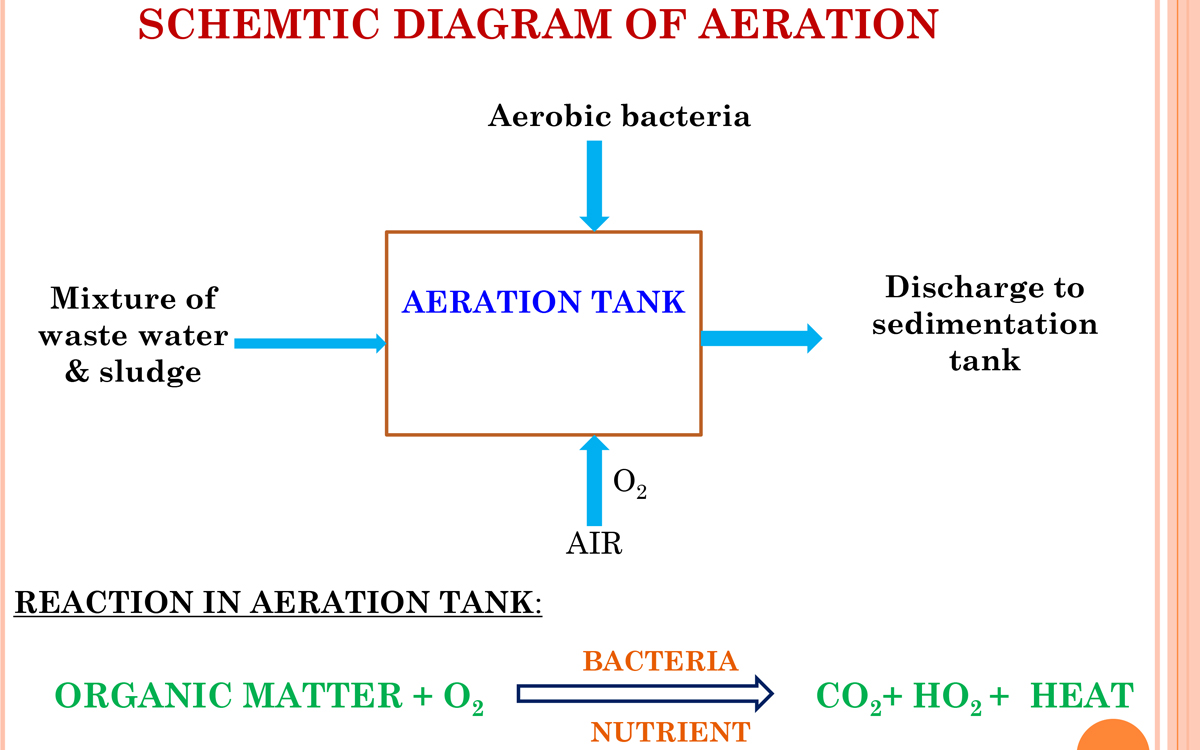
6. Aeration tank
- The water is passed like a thin film over the different arrangements like staircase shape.
- Dosing of Urea and DAP is done.
- Water gets direct contact with the air to dissolve the oxygen into water.
- BOD & COD values of water is reduced up to 90%.
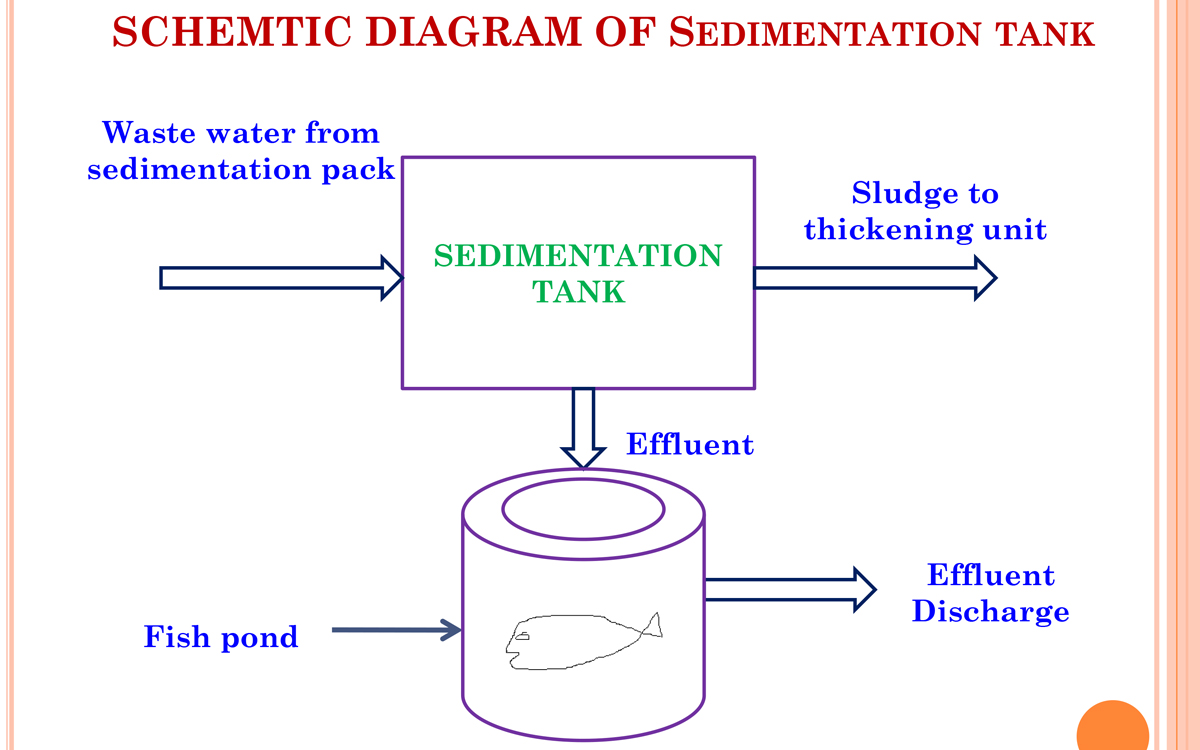
7. Clarifier
- The clarifier collects the biological sludge.
- The overflowed water is called as treated effluent and disposed out.
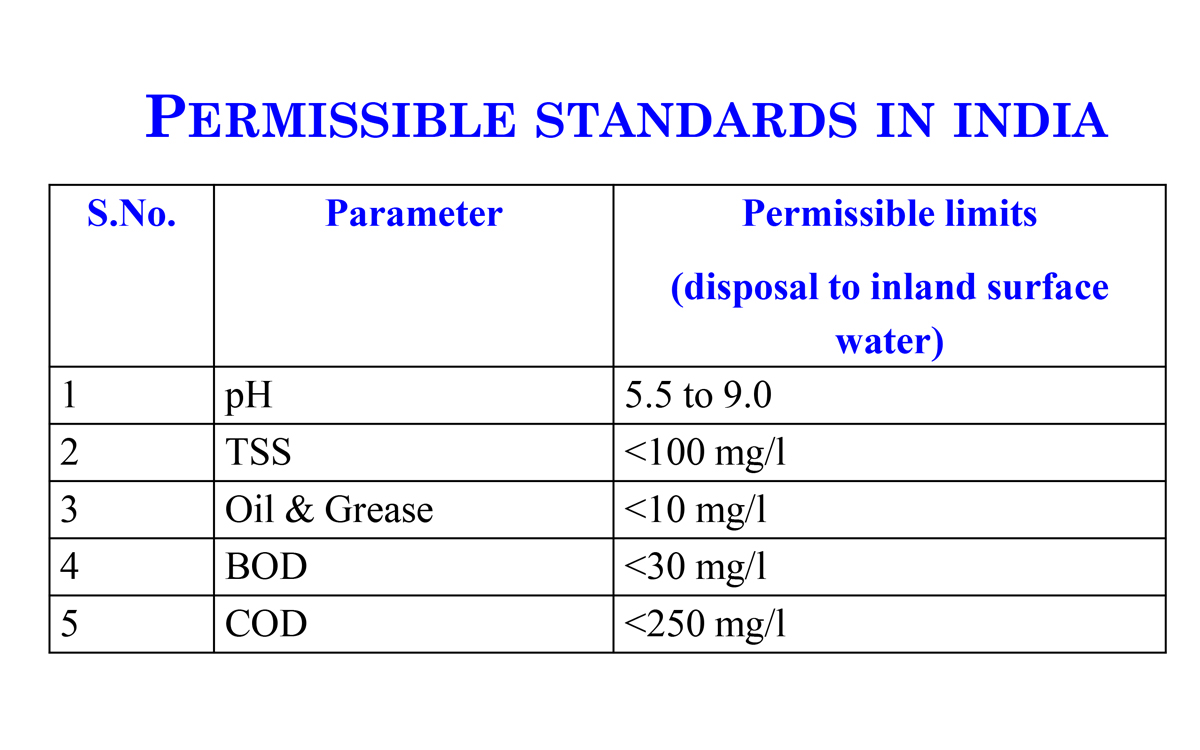
- The outlet water quality is checked to be within the accepted limit as delineated in the norms of the Bureau of Indian standards.
- Through pipelines, the treated water is disposed into the environment river water, barren land, etc.
- ETP Plant Operation
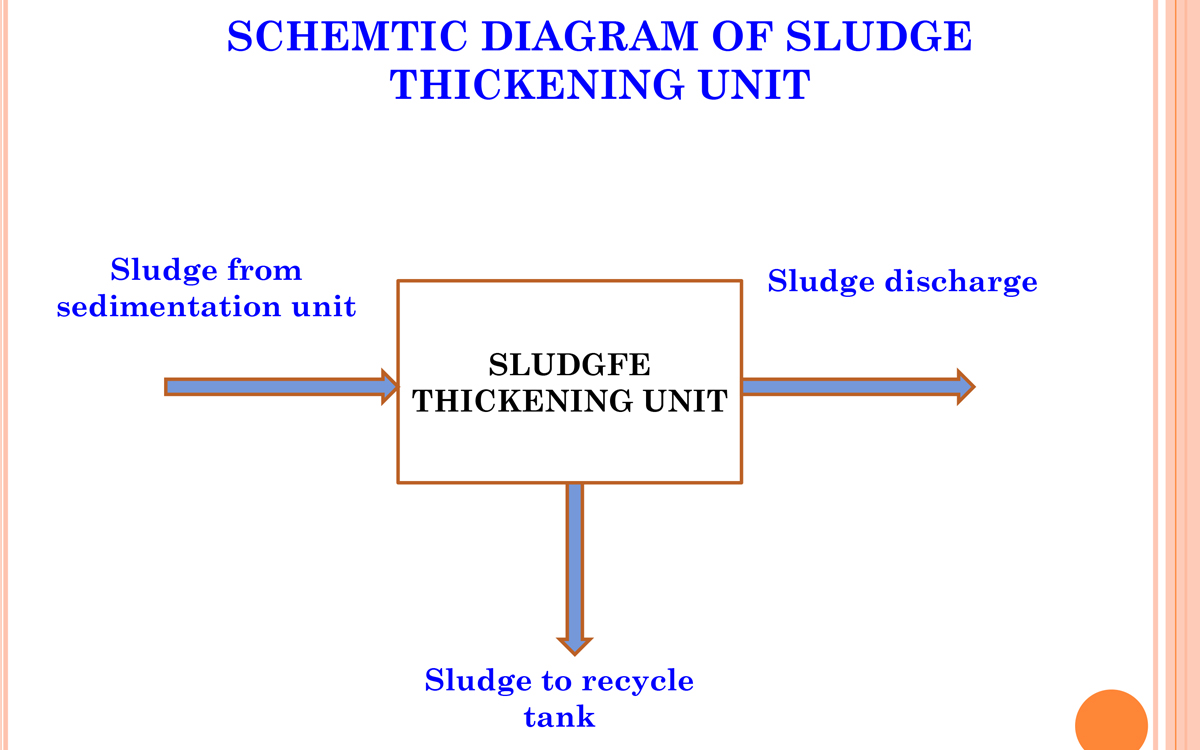
8. Sludge thickener
- The inlet water consists of 60% water + 40% solids.
- The effluent is passed through the centrifuge.
- Due to centrifugal action, the solids and liquids are separated.
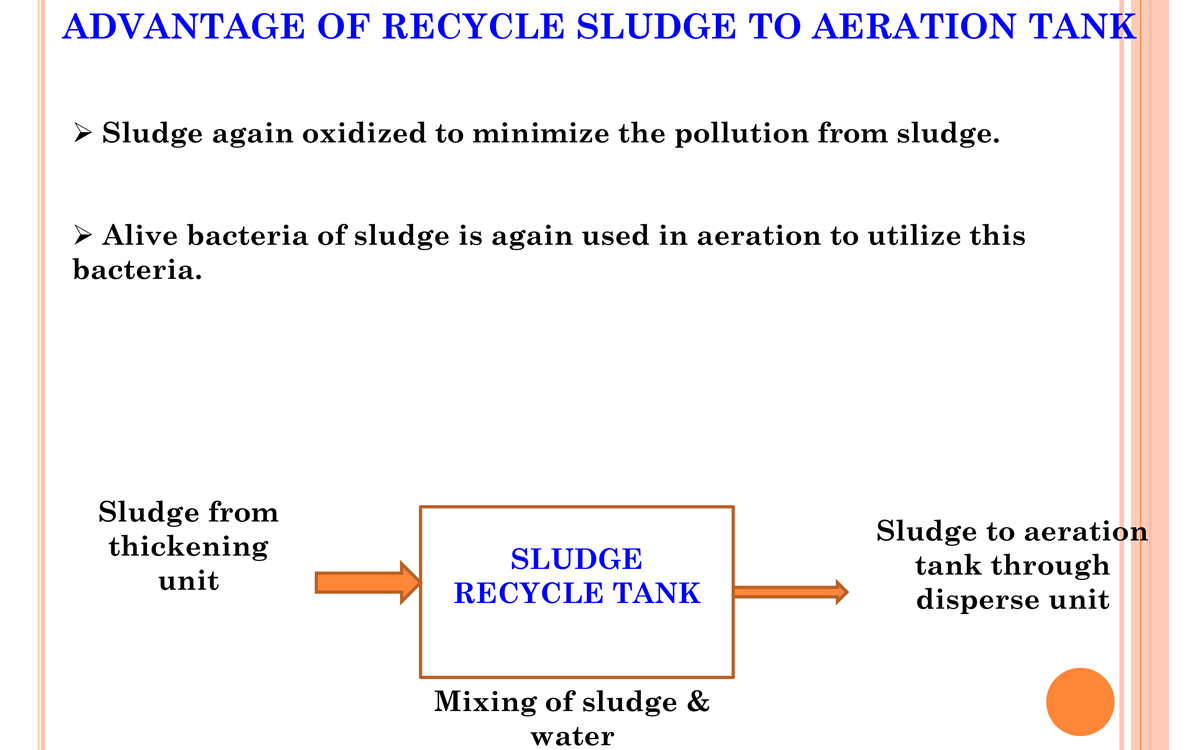
- The sludge thickener reduces the water content in the effluent to 40% water + 60% solids.
- The effluent is then reprocessed and the sludge collected at the bottom.
9. Drying beds
- Primary and secondary sludge is dried on the drying beds.
Working Flow Chart Of ETP Plants (Effluent Treatment Plant)
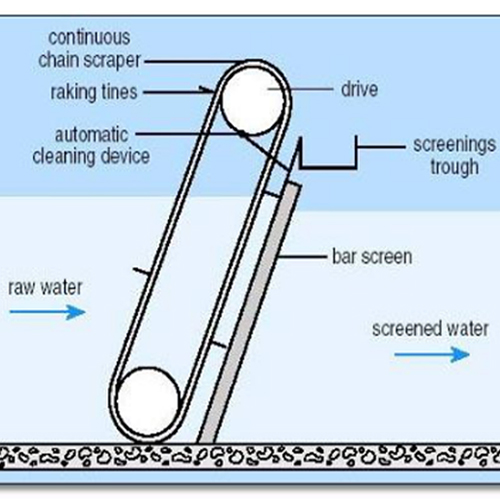
SCREENING
- Screening is the filtration process for the separation of coarse particles from influent.
- Stainless steel net with varying pore size can be utilized.
- Screens are cleaned regularly to avoid clogging.